Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
September 12, 2023A serious medical condition known as deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, commonly in the legs. This article aims to offer comprehensive insights into DVT, from its causes and symptoms to effective treatments. Being informed is the first step in taking proactive measures for your vascular health.
What Exactly is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Blood clot formation in a deep vein is known as deep vein thrombosis, or DVT. These veins are not the ones you see just under the skin; they are located deeper, within the muscles. Such a vein clot is a serious medical problem that needs to be treated right once.
Decoding the Meaning of DVT
Deep Vein Thrombosis is referred to as “DVT” in shorthand. In medical jargon, “thrombosis” denotes the development of a blood clot, and “deep vein” designates the location of the clot. Knowing the meaning of DVT will help you appreciate how serious this issue is.
Uncovering the Causes
The emergence of DVT can be attributed to numerous circumstances. Prolonged periods of immobility, such as long flights or bed rest, can lead to clot formation. Surgical procedures or injuries that affect the veins can also result in DVT. Other contributing variables include certain medical illnesses including cancer and heart disease as well as genetic predispositions.
Recognizing the Signs: The First Step in Addressing DVT
One of the most crucial steps in dealing with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is recognizing its symptoms early on. Early detection can lower the risk of serious complications and considerably improve the outcome. The symptoms of DVT can vary in intensity and may develop gradually or suddenly. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Pain or Tenderness in the Affected Leg
One of the first signs of DVT is often a throbbing or cramping pain in the affected leg, usually starting in the calf. The pain may start mild and become more severe over time, or it could be intense right from the beginning. - Swelling in the Leg or Ankle
Swelling is another common symptom of DVT. The swelling typically occurs in one leg and may be accompanied by a heavy ache. It’s essential to compare both legs and look for noticeable differences in size. - Red or Discolored Skin
The skin around the clot may become discolored, taking on a reddish or even bluish tint. It is important to pay attention to this discolouration since it indicates decreased blood flow. - Warm Sensation Over the Clot Area
You may notice a localized warm area over the site of the clot. This warmth is caused by inflammation and increased blood flow to the affected area as the body tries to heal itself.
Symptoms Specific to Blood Clots in Deep Veins
It’s crucial to distinguish between general symptoms of blood clots and those unique to DVT. While some symptoms may overlap, those of DVT are usually localized to the leg where the clot has formed. For example, superficial clots that occur closer to the skin’s surface may not exhibit the same level of pain or swelling as deep vein thrombosis.
Warning Signs of a Leg Blood Clot: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Severe symptoms, such as excruciating pain, notable swelling, or obvious discoloration in the leg, could be an indication of a dangerous blood clot that has to be treated right once. Other alarming symptoms may include:
- Sudden onset of shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort, especially when taking deep breaths
- Unexplained cough, sometimes with bloody mucus
These symptoms could be an indication that the blood clot has moved from the leg to the lungs, which would greatly increase the risk of pulmonary embolism. In these circumstances, prompt medical care is crucial.
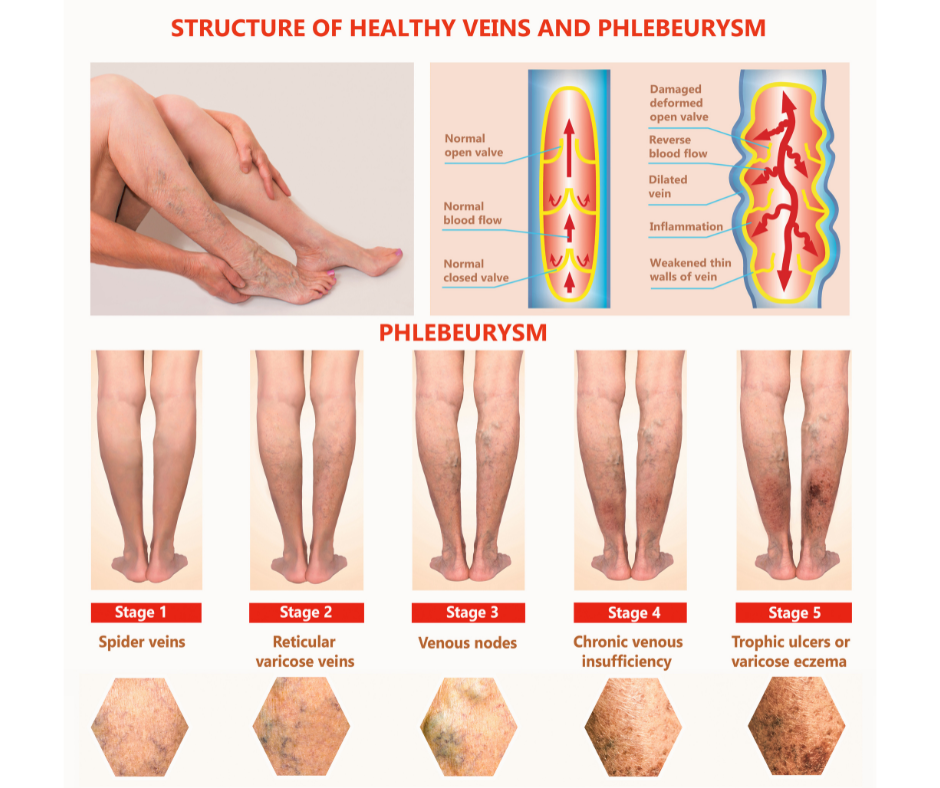
Factors Associated With Risk
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing DVT. Older age groups are generally at higher risk. Being overweight increases the risk by adding to the pressure on your leg veins. Pregnancy-related hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and cigarette use, which affects blood coagulation and vein health, can all be factors.
Active Vascular Health Measures
Deep vein thrombosis is not to be taken lightly. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and potential treatments of the condition will help you take preventative measures to avoid negative effects. Always consult your healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
The Role of Lifestyle Choices in DVT Prevention
Although medical treatments are essential for managing DVT, a person’s lifestyle can also have a significant impact on prevention. Improved vascular health can be attained with a balanced diet, consistent exercise, and quitting smoking. Even easy exercises like walking can increase blood flow and lower the chance of clot development.
Available Treatment Options
When it comes to treating deep vein thrombosis (DVT), the primary goal is to prevent the blood clot from enlarging and causing more severe complications like a pulmonary embolism. A blood clot that escapes and travels to the lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal. Here are some of the most common treatment options for DVT:
Anticoagulants: The First Line of Defense
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are usually the first course of treatment for DVT. These medications don’t actually “thin” the blood but rather decrease its ability to clot. Common anticoagulants include warfarin and heparin. When taking these medications, it’s very important to carefully follow your doctor’s recommendations because failing to do so could result in severe bleeding or other issues.
Compression Stockings: Aiding Blood Flow
Compression stockings are specially designed to improve blood flow in the legs, reducing the symptoms of DVT. These stockings apply pressure to the lower legs, helping to reduce swelling and discomfort. They are frequently combined with anticoagulants to effectively control DVT symptoms.
Thrombolytics: Clot Dissolvers
In more severe cases of DVT, thrombolytic drugs may be used. These are powerful medications that can dissolve blood clots quickly. However, they come with a higher risk of bleeding and are generally reserved for more serious cases where immediate clot dissolution is necessary.
Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis: A Minimally Invasive Option
During this treatment, a catheter is inserted into the veins and advanced to the location of the blood clot. Thrombolytic medication is then delivered directly to the clot to dissolve it. This is a less invasive option but still carries some risks, including bleeding and infection.
Surgical Intervention: A Last Resort
In extreme cases of deep vein thrombosis where the blood clot poses an immediate threat to life, surgical intervention becomes not just an option but a critical necessity. A thrombectomy is a surgical operation in which the blood clot is directly removed from the deep vein.
Thrombectomy is generally considered a last resort for several reasons:
- Immediate Risk: This procedure is usually reserved for situations where there is a high risk of the clot causing a pulmonary embolism, which could be fatal.
- Failure of Other Treatments: Thrombectomy is considered when anticoagulants and thrombolytic medications have failed to dissolve the clot, or when these medications pose too high a risk due to other medical conditions.
- Location and Size of the Clot: The surgical option is more likely to be considered if the blood clot is large or located in a position that makes it particularly dangerous, such as near the lungs.
- Medical Complications: Patients with other severe medical conditions that make the use of anticoagulants or thrombolytics risky may be candidates for surgical removal of the clot.
- Urgency: In cases where time is of the essence, surgical intervention can be the quickest way to remove a dangerous clot, thereby preventing severe complications like a pulmonary embolism.
The Procedure
The thrombectomy procedure involves making an incision to access the vein containing the clot. Specialized surgical instruments are then used to remove the clot carefully. The vein may be repaired with sutures or left to heal naturally, depending on the specific circumstances.
Risks and Aftercare
Thrombectomy has its own set of dangers, including infection, excessive bleeding, and negative anesthetic reactions, just like any surgical surgery. Therefore, it’s critical to properly balance the dangers and advantages. Post-operative care often involves the use of anticoagulants to prevent new clots from forming, as well as regular monitoring to ensure that the vein heals properly.
Understanding the DVT treatment options available will help you and your healthcare professional decide on the best course of action for your situation. Always consult a medical professional for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.The Emotional Toll of DVT
It’s critical to recognize the psychological and emotional effects of a DVT diagnosis. Both the sufferer and their loved ones may experience severe stress and worry as a result of the condition.Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends can be invaluable in navigating the emotional aspects of DVT.
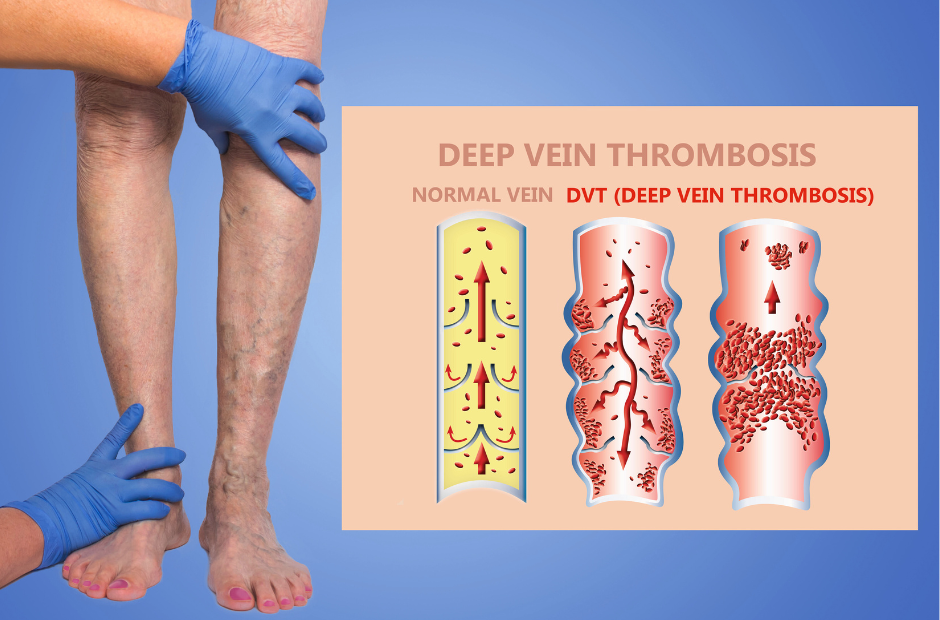
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
The therapy of deep vein thrombosis depends heavily on early diagnosis. The sooner DVT is identified, the better the chances of preventing severe complications such as a pulmonary embolism. If you experience any symptoms of a blood clot in your leg, consult a healthcare provider immediately for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests for DVT
When you consult a healthcare provider for suspected DVT, several diagnostic tests may be conducted. These often include ultrasound imaging to visualize the blood clot and blood tests to measure certain clotting factors. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent complications.
The Role of Family History in DVT
Your chance of acquiring DVT can be considerably increased by a family history of vein thrombosis. If you have close relatives who have had DVT, it’s crucial to discuss this with your healthcare provider. They may recommend regular screenings or other preventive measures.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms of blood clot in leg, such as severe pain, swelling, or discoloration, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Delaying treatment can result in serious problems, including the possibility that the clot will spread to the lungs and result in a potentially fatal pulmonary embolism.
The Importance of Ongoing Monitoring
Following a deep vein thrombosis diagnosis, continued monitoring is essential. Your healthcare provider will likely recommend regular check-ups to assess the effectiveness of your treatment plan. Blood tests to assess your body’s reaction to anticoagulants and ultrasound scans to examine the size and location of the blood clot in your leg may be part of monitoring.
Summary and Final Thoughts
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious medical condition that necessitates constant monitoring. From recognizing the early symptoms of a blood clot in the leg to understanding the available treatment options, being informed is your first line of defense. Lifestyle choices, early diagnosis, emotional support, and ongoing monitoring play significant roles in managing DVT effectively. Always consult your healthcare provider for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
