Understanding Venous Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
July 5, 2023Introduction
A frequent disorder called venous insufficiency impairs blood flow in the veins, especially in the lower limbs. This condition occurs when the valves within the veins become weak or damaged, leading to poor blood flow and a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. In this article we will examine the origins, signs, and symptoms of venous insufficiency, enabling you to take proactive measures to enhance your vascular health and general wellbeing.
Causes of Venous Insufficiency
Venous insufficiency can be attributed to several underlying causes, each contributing to the impairment of venous blood flow and the development of this condition. Understanding these causes is essential for identifying risk factors and taking appropriate preventive measures. Let’s delve deeper into the primary causes of venous insufficiency:
Dysfunction of Vein Valves
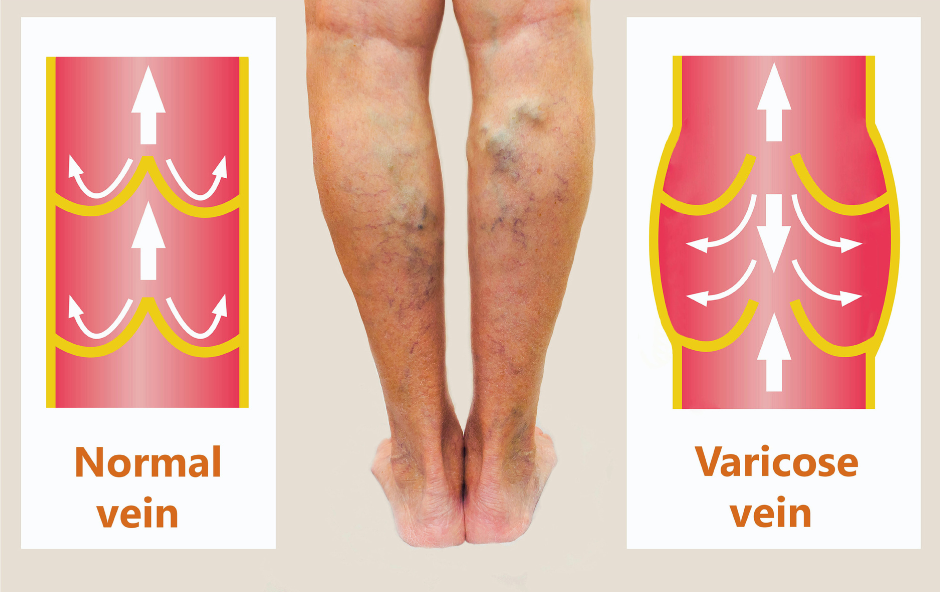
The normal function of veins relies on one-way valves that help propel blood towards the heart. When these valves weaken or are damaged, they are unable to shut correctly, which causes blood to flow backward and then collect in the veins. Over time, this leads to venous insufficiency. The weakening of vein valves can occur due to factors such as genetics, aging, or prolonged pressure on the veins.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
The term “deep vein thrombosis” refers to the formation of blood clots in deep veins, usually in the legs or pelvis. These clots can obstruct blood flow and cause injury to the vein valves. DVT can lead to the onset of venous insufficiency if it is not managed. Long-term immobility, trauma, some medical illnesses (including cancer or clotting disorders), and hormonal aspects (like pregnancy or the use of hormonal contraception) are also risk factors for DVT.
Pregnancy
The risk of having venous insufficiency can increase due to the physiological changes that occur during pregnancy. Hormonal fluctuations, accurately an increase in progesterone levels, can cause the walls of the veins to relax, leading to diminished vein tone and reduced valve functionality. Furthermore, when the uterus grows, it puts pressure on the veins in the pelvis and lower legs, which restricts blood flow and encourages the growth of varicose veins and venous insufficiency.
Obesity and Excessive Weight
Carrying excess body weight puts additional strain on the veins, making it harder for them to efficiently return blood to the heart. This increased pressure and compromised venous circulation can weaken vein walls and valves, promoting the development of venous insufficiency.
Prolonged Sitting or Standing
Occupations or activities that involve prolonged periods of sitting or standing can impede blood circulation, mostly in the lower extremities. Blood pools and venous insufficiency result when the leg muscles are inactive for long periods of time because they are less efficient at moving blood back towards the heart. Jobs that require long hours of sitting or standing, such as office work or professions in hospitality or retail, can significantly contribute to the development of venous insufficiency.
Prior Vein Trauma or Surgery
Previous injuries or surgeries that involve the veins can lead to structural damage or scarring, compromising vein functionality and increasing the risk of venous insufficiency. Invasive procedures such as vein stripping or trauma resulting from accidents or surgeries can disrupt normal blood flow and impair vein valves, predisposing individuals to venous insufficiency.
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal changes or imbalances can impact vein health and contribute to venous insufficiency. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone can relax vein walls, making them more susceptible to stretching and valve dysfunction. Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can exacerbate venous insufficiency symptoms.
Most people can recognize potential risk factors and take steps to prevent or manage the illness by being aware of the causes of venous insufficiency. People have the opportunity to reduce their risk of developing venous insufficiency and they can improve their vascular health by addressing these underlying causes and implementing healthy lifestyle practices like consistent exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding extended periods of inactivity or extended standing. Moreover, early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing venous insufficiency effectively, preventing complications, and enhancing overall well-being.
Symptoms and Warning Signs of Venous Insufficiency
Venous insufficiency is a condition characterized by impaired blood flow in the veins, mainly in the lower extremities. It is essential to recognize the symptoms and warning signs of venous insufficiency in order to be able to intervene in time. Here are the common symptoms that individuals may experience:
Varicose Veins symptoms
Varicose veins are one of the primary visible indicators of venous insufficiency. They appear as enlarged, twisted veins that are often bluish or purple in color. Varicose veins may be raised or bulging and can be seen just beneath the surface of the skin. These veins may cause discomfort, heaviness, or aching in the legs.
Leg Pain and Discomfort
Individuals with venous insufficiency often experience leg pain and discomfort. The pain is typically described as aching, throbbing, or a sense of heaviness in the affected leg or legs. The discomfort may worsen after prolonged periods of standing or sitting and may improve with leg elevation or walking.
Swelling and Edema
Swelling, medically known as edema, is a common symptom of venous insufficiency. The impaired blood flow in the affected veins can result in fluid retention, leading to swelling in the lower legs, ankles, and feet. The swelling may worsen as the day progresses and improve with leg elevation.
Skin Changes
Because of venous insufficiency we can see some changes in the skin surrounding the affected veins. The skin may appear discolored, typically with a reddish-brown hue. Sometimes, the skin may become dry, itchy, or irritated. Prolonged venous insufficiency can result in the development of skin ulcers or open sores.
Skin Ulcers
In severe cases of venous insufficiency, skin ulcers may develop. These ulcers typically occur near the ankles and are often referred to as venous stasis ulcers or venous leg ulcers. They can be painful, slow to heal, and prone to infection. If left untreated, skin ulcers can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is a condition characterized by uncomfortable sensations in the legs, often described as a crawling, itching, or tingling sensation. Individuals with venous insufficiency may experience RLS symptoms, particularly during periods of inactivity or at night when trying to sleep.
Heavy or Fatigued Legs
Individuals with venous insufficiency may experience a persistent feeling of heaviness or fatigue in the legs. This sensation may worsen with prolonged standing or sitting and can significantly impact daily activities and mobility.
It’s crucial to remember that each person will experience symptoms differently, both in terms of severity and combination. For a precise diagnosis and the most suitable course of action, it is advised that you speak with a healthcare provider with expertise in vascular health if you are exhibiting any of these symptoms.
Early detection and intervention are key to managing venous insufficiency effectively. Treatment possibilities may include lifestyle modifications, such as consistent exercise, elevation of the legs, and weight management. Compression therapy, medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery may also be considered based on the severity of the condition.
Individuals can take control of their vascular health, ease discomfort, and avoid consequences related to venous insufficiency by being aware of the signs and getting prompt medical help.
Effective Treatment Options for Venous Insufficiency
When it comes to managing venous insufficiency and alleviating its symptoms, several effective treatment options are available. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, individual patient factors, and the recommendation of a healthcare professional. Let’s explore some of the commonly used treatment approaches:
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing venous insufficiency. These modifications may include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve blood circulation in the legs. Exercise promotes the contraction of leg muscles, aiding in the pumping of blood back to the heart.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins and hampers proper blood flow. Losing weight, if necessary, can help reduce the burden on the veins and alleviate symptoms.
- Leg Elevation: Elevating the legs above the heart level several times a day can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow. It is particularly beneficial to elevate the legs while resting or sleeping.
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is a widely recommended treatment for venous insufficiency. It involves the use of compression stockings or garments that apply gentle pressure to the legs, helping to improve blood flow and prevent blood from pooling in the veins. Compression garments come in various strengths and lengths, and their selection depends on the severity of the condition and individual patient needs.
- Compression Stockings: These elastic stockings are designed to provide graduated compression, with the highest pressure at the ankles gradually decreasing towards the thighs. They help promote blood flow, reduce swelling, and alleviate symptoms such as leg pain and fatigue. Compression stockings are available in different styles, including knee-high, thigh-high, and pantyhose.
- Compression Bandages: In more severe cases or when ulcers are present, healthcare professionals may recommend the use of multi-layer compression bandages. These bandages provide higher levels of compression and are often used in conjunction with other treatments to promote wound healing.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or treat underlying conditions associated with venous insufficiency. These medications may include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with venous insufficiency. They are particularly useful in relieving discomfort caused by swollen or inflamed veins.
- Anticoagulants: If venous insufficiency is associated with deep vein thrombosis (DVT), anticoagulant medications may be prescribed. These medications help prevent blood clots from forming or growing larger, reducing the risk of complications.
- Topical Ointments or Creams: Certain topical preparations containing ingredients like horse chestnut seed extract or witch hazel may provide symptomatic relief, including reducing swelling and discomfort.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
In cases where lifestyle modifications and conservative measures are insufficient, minimally invasive procedures may be considered to treat venous insufficiency. These procedures are performed on an outpatient basis and involve minimal discomfort and recovery time. Some common minimally invasive treatments include:
- Endovenous Ablation: This procedure uses heat energy (radiofrequency or laser) to close off the affected vein. By sealing the damaged vein, blood flow is redirected to healthier veins, relieving symptoms and reducing the appearance of varicose veins.
- Sclerotherapy: Sclerotherapy involves injecting a sclerosing solution directly into the affected veins. The solution causes irritation and scarring within the vein, leading to its closure and eventual absorption by the body. Sclerotherapy is often used for smaller varicose veins and spider veins.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Ambulatory phlebectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of superficial varicose veins through tiny incisions. It is typically performed under local anesthesia and offers effective and immediate relief from symptoms.
Surgical Interventions:
In rare cases, when other treatments have not been successful or if complications arise, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options include: - Vein Ligation and Stripping: This procedure involves tying off and removing the affected vein through small incisions. It is typically reserved for severe cases of venous insufficiency and larger varicose veins.
- Vein Bypass: In some situations, a vein bypass surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves creating a new pathway for blood to bypass the damaged vein and restore proper blood flow.
To find the best course of action for your unique problem, it’s crucial to speak with a medical expert with expertise in vascular health. They will evaluate the extent of your venous insufficiency, take into account your medical background, and provide a customized treatment strategy.
In conclusion, effective management of venous insufficiency involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, conservative measures, and various treatment options. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, using compression therapy, considering medications when necessary, and exploring minimally invasive procedures or surgical interventions, individuals can alleviate symptoms, improve blood flow, and enhance their vascular health. Always seek the advice of a medical practitioner for a precise diagnosis and direction on the best course of action for treating your venous insufficiency.
