Understanding Stroke: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
July 13, 2023Introduction:
Stroke (cerebrovascular accident) is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention and appropriate treatment. It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, leading to the death of brain cells and potentially causing long-term disabilities. While traditional treatments for stroke focus on medication and rehabilitation, vascular surgery has emerged as a promising approach in certain cases. In this article, we will explore the role of vascular surgery in the treatment of stroke and its potential benefits for patients.
Different Stroke Types:
First we must clarify what is a stroke, which is also called as a cerebrovascular accident. Stroke can be classified into different types, each with its own distinct characteristics and underlying causes. Understanding the various stroke types is essential for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures. Furthermore it is even more important to know the signs of a stroke to be able to make the proper medical steps. Let’s explore the different types of stroke and the signs of a stroke, especially the brain stroke symptoms in more detail.
Ischemic Stroke:
Ischemic stroke is the most common type, accounting for approximately 87% of all strokes. It occurs when a blood clot or other blockage obstructs a blood vessel, leading to a significant reduction or complete cessation of blood flow to the brain. This lack of blood supply deprives the brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, causing cellular damage and potentially severe neurological deficits showing up in several symptoms of brain stroke. Common causes of ischemic stroke include blood clots forming in the brain’s blood vessels (thrombosis), embolisms traveling from other parts of the body (such as the heart or large arteries) to the brain, and stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid or cerebral arteries.
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or leaks, leading to bleeding in or around the brain. It accounts for approximately 13% of all strokes. There are two main types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: This type of hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel within the brain ruptures, causing bleeding within the brain tissue. The bleeding can result from conditions such as high blood pressure (hypertension), blood vessel abnormalities, or the use of blood-thinning medications. Intracerebral hemorrhage often leads to localized brain damage and can be life-threatening.
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Subarachnoid hemorrhage is characterized by bleeding into the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering it. This type of hemorrhage is typically caused by the rupture of an aneurysm (a weakened area in the blood vessel wall) or arteriovenous malformation (AVM). Subarachnoid hemorrhage can cause a sudden and severe headache, and it requires immediate medical attention.
Some common symptoms of brain stroke to be aware of:
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: One of the most common symptoms of a brain stroke is sudden weakness or numbness, typically affecting one side of the body. It may manifest as weakness or heaviness in the face, arm, or leg. For example, you may notice difficulty raising an arm or experiencing a drooping sensation on one side of the face. This symptom occurs due to the disruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to a loss of motor function in the affected areas.
- Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech: A brain stroke can impair the ability to speak or understand speech. Individuals experiencing a stroke may have trouble finding the right words, slurred speech, or difficulty understanding what others are saying. This symptom, known as aphasia, occurs when the areas of the brain responsible for language processing are affected by the stroke.
- Vision Problems: Vision disturbances or sudden changes in vision can also indicate a brain stroke. These may include blurred vision, double vision, or a loss of vision in one or both eyes. The visual impairments occur due to the disruption of blood flow to the areas of the brain responsible for vision.
- Severe Headache: A sudden and severe headache, often described as the worst headache of one’s life, can be a warning sign of a brain stroke. This intense headache typically occurs abruptly and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or altered consciousness. It is important to note that not all strokes present with a headache, but its presence, particularly if severe and unusual, should be taken seriously.
- Loss of Balance or Coordination: A brain stroke can affect a person’s balance and coordination. Individuals may experience dizziness, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, and a sense of unsteadiness. This symptom occurs when the stroke affects the regions of the brain responsible for coordinating movement and balance.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA):
A transient ischemic attack, often referred to as a “mini-stroke,” is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain. While TIAs do not cause permanent brain damage, they serve as a warning sign for an increased risk of a full-blown stroke in the future. The symptoms of a TIA are similar to those of an ischemic stroke but typically resolve within a short period, usually lasting only a few minutes to a few hours. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are crucial following a TIA to prevent a subsequent stroke.
Understanding what is a stroke and the different types of stroke enables healthcare professionals to tailor appropriate treatments and preventive measures based on the specific characteristics and underlying causes. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and timely intervention are essential in improving outcomes and minimizing the long-term impact of stroke on individuals’ lives.
Understanding the Causes of Stroke:
There are quite a few explanation of what causes a stroke. Stroke is a complex medical condition that can have devastating consequences for individuals and their families. It is important to gain a comprehensive understanding of the causes and mechanisms behind stroke in order to effectively prevent, diagnose, and treat this life-threatening event. Let’s explore what causes a stroke and the symptoms associated with it, and the different types of stroke.
Understanding the causes of stroke is crucial for developing preventive measures and identifying individuals at risk. Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of a stroke that we will further explore in this article.
Ischemic Stroke Causes:
Ischemic stroke is the most common type, accounting for approximately 87% of all strokes. It occurs when a blood clot obstructs a blood vessel, reducing or completely blocking blood flow to the brain. Common causes of ischemic stroke include:
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in the arteries that supply blood to the brain, leading to a blockage. These clots can originate from various sources, such as the heart, where they form due to conditions like atrial fibrillation or heart valve disorders.
- Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances in the arteries, forming plaques. When these plaques rupture or become dislodged, they can cause a blockage in the blood vessels supplying the brain.
- Small Vessel Disease: Small vessel disease occurs when the small blood vessels in the brain narrow or become damaged, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of stroke.
Hemorrhagic Stroke Causes:
Hemorrhagic stroke accounts for approximately 13% of all strokes and occurs when a blood vessel ruptures or leaks in the brain. Common causes of hemorrhagic stroke include:
- High Blood Pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can weaken blood vessel walls over time, increasing the risk of rupture and bleeding in the brain.
- Aneurysms: An aneurysm is a weakened area in the wall of a blood vessel that can balloon and eventually rupture, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): AVMs are abnormal tangles of blood vessels that can disrupt normal blood flow and increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
Recognizing the stroke signs is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Common stroke signs include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body).
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
Severe headache without a known cause. - Sudden confusion or trouble with vision.
- Trouble walking, loss of balance, or coordination difficulties.
It is important to remember that these stroke symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the stroke. If any of these symptoms occur, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention by calling emergency services.
The Role of Vascular Surgery in Stroke Treatment:
Vascular surgery plays a critical role in the treatment of stroke, particularly in cases of ischemic stroke. By addressing the underlying vascular issues, vascular surgery offers potential solutions to improve blood flow and minimize the risk of further complications. Let’s explore the different techniques and procedures used in vascular surgery for stroke treatment.
Carotid Endarterectomy:
Carotid endarterectomy is a commonly performed vascular surgery procedure for patients with ischemic stroke. This procedure involves removing plaque buildup from the carotid arteries located in the neck. Plaque accumulation in these arteries can lead to reduced blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of stroke. Carotid endarterectomy effectively removes the plaque, restoring normal blood flow and reducing the likelihood of future strokes.
Endovascular Thrombectomy:
Endovascular thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat ischemic stroke caused by a blood clot. In this procedure, a catheter is inserted into the blocked artery through a small incision, allowing the surgeon to physically remove the clot or use specialized tools to break it up. Endovascular thrombectomy is highly effective when performed within the early hours of stroke onset, ideally within the “golden hour” timeframe. It has shown significant success in restoring blood flow to the brain and minimizing the extent of brain damage.
Carotid Artery Stenting:
Carotid artery stenting is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat carotid artery disease, a condition where the carotid arteries in the neck become narrowed or blocked. These arteries supply blood to the brain, and when they are affected by atherosclerosis or plaque buildup, it can increase the risk of stroke. Carotid artery stenting involves the placement of a stent, a small mesh-like tube, to widen the narrowed artery and improve blood flow to the brain.
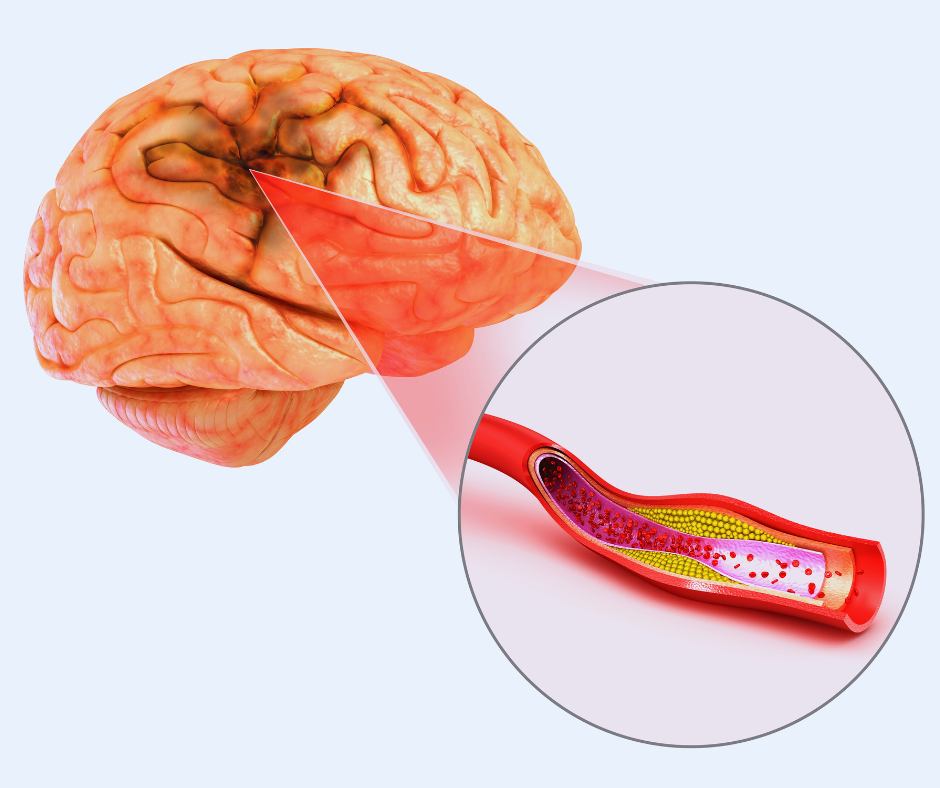
Benefits of Vascular Surgery for Stroke Patients:
Vascular surgery offers several significant benefits for patients suffering from stroke, particularly in cases of ischemic stroke. By addressing the underlying vascular issues, vascular surgery interventions can provide potential solutions to improve blood flow, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance the overall prognosis. Let’s delve deeper into the key benefits of vascular surgery for stroke patients, incorporating the previously mentioned keywords.
Improved Blood Flow:
Vascular surgery plays a crucial role in restoring and improving blood flow to the brain. In cases of ischemic stroke, where a blood clot obstructs an artery, procedures such as carotid endarterectomy and endovascular thrombectomy effectively address the blockage. By removing plaque buildup or blood clots, these interventions restore normal blood flow, reducing the risk of further damage to brain tissue and improving overall brain function.
Reduced Risk of Recurrent Stroke:
One of the primary benefits of vascular surgery for stroke patients is the significant reduction in the risk of recurrent strokes. Carotid endarterectomy, for example, removes the plaque buildup in the carotid arteries, which is a common site for blockages leading to strokes. By eliminating the blockage, the procedure significantly decreases the likelihood of future stroke events, providing patients with a better long-term prognosis and reducing the associated risks and disabilities.
Enhanced Stroke Recovery:
Vascular surgery interventions can contribute to a faster and more successful recovery from stroke. Prompt restoration of blood flow to the brain is crucial in minimizing the extent of brain damage and preserving brain tissue. By promptly addressing the blockage and restoring blood flow, vascular surgery procedures, such as endovascular thrombectomy, have shown promising results in preserving neurological function and minimizing long-term neurological deficits. This enhances the overall stroke recovery process and improves the patient’s quality of life.
Prevention of Long-Term Disabilities:
By improving blood flow and reducing the risk of recurrent strokes, vascular surgery interventions help prevent long-term disabilities associated with stroke. The brain relies on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients delivered by the blood. Restoring blood flow promptly and effectively through vascular surgery minimizes the risk of extensive brain damage and subsequent disabilities such as paralysis, speech impairments, cognitive deficits, and mobility limitations. The ability to prevent or minimize these disabilities significantly enhances the patient’s functional outcomes and overall independence.
Personalized Treatment Approach:
Vascular surgery for stroke patients offers a personalized treatment approach that takes into account the individual’s specific condition, needs, and medical history. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals assesses the patient’s eligibility and tailors the surgical intervention accordingly. This personalized approach ensures that the most appropriate procedure is chosen to address the underlying vascular issues and optimize the patient’s outcomes.
Vascular surgery provides significant benefits for stroke patients, particularly in cases of ischemic stroke. The interventions aimed at improving blood flow, reducing the risk of recurrent stroke, enhancing stroke recovery, and preventing long-term disabilities. By promptly addressing the underlying vascular issues through procedures like carotid endarterectomy and endovascular thrombectomy, vascular surgeons play a vital role in improving patient outcomes, minimizing the risks associated with stroke, and ultimately enhancing the quality of life for stroke patients.
Eligibility for Vascular Surgery:
Determining the eligibility for vascular surgery in stroke patients involves a comprehensive evaluation by a team of medical professionals. Several factors are considered to ensure the appropriateness and potential benefits of the surgical intervention. Let’s explore the key considerations and factors that influence the eligibility for vascular surgery in the treatment of stroke.
Type of Stroke:
The type of stroke is an important factor in determining eligibility for vascular surgery. Ischemic strokes, caused by blood clots or plaque buildup, are more likely to be considered for vascular surgical interventions. Hemorrhagic strokes, which involve bleeding in or around the brain, may have different treatment approaches that may not involve vascular surgery.
Location of the Blockage:
The location of the blockage within the blood vessels supplying the brain is another critical aspect. Carotid arteries, for instance, are common sites for blockages that can be addressed through carotid endarterectomy. If the blockage is inaccessible or involves smaller blood vessels, other treatment options may be explored.
Time Since Stroke Occurred:
The time that has elapsed since the stroke occurred is a crucial factor in determining eligibility for vascular surgery. Certain procedures, such as endovascular thrombectomy, are time-sensitive and are most effective when performed within a specific timeframe after the stroke, commonly known as the “golden hour.” Beyond that timeframe, the risks and benefits of the surgery need to be carefully evaluated.
Overall Health and Medical History:
The patient’s overall health and medical history play a significant role in determining eligibility for vascular surgery. Factors such as age, existing medical conditions (e.g., heart disease, kidney disease), previous surgeries, and medications can impact the decision-making process. A comprehensive assessment of the patient’s health helps determine the surgical risks and potential benefits.
Consultation with a Multidisciplinary Team:
The decision to undergo vascular surgery in stroke cases is typically made by a multidisciplinary team of medical professionals, including neurologists, vascular surgeons, and interventional radiologists. These experts collaborate to evaluate the patient’s specific circumstances, review diagnostic imaging, and discuss potential treatment options. Their collective expertise ensures a comprehensive evaluation and a well-informed decision regarding the appropriateness of vascular surgery.
Patient Preferences and Informed Consent:
The patient’s preferences and goals of care are essential considerations in the decision-making process. The medical team should engage in open and honest discussions with the patient and their family, providing clear explanations of the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of vascular surgery. Informed consent is obtained after thoroughly discussing all available options, including non-surgical treatments and alternative approaches.
Determining the eligibility for vascular surgery in stroke patients requires a thorough assessment by a multidisciplinary team. Factors such as the type of stroke, location of the blockage, time since stroke occurrence, overall health, and patient preferences are carefully considered. By taking into account these factors and engaging in informed decision-making, the medical team can determine whether vascular surgery is an appropriate intervention that offers potential benefits in terms of improving blood flow, reducing the risk of recurrent stroke, and enhancing stroke recovery.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, vascular surgery has emerged as a crucial and promising approach in the treatment of stroke, particularly in cases of ischemic stroke. Procedures such as carotid endarterectomy and endovascular thrombectomy have demonstrated significant benefits in improving blood flow, reducing the risk of recurrent strokes, and enhancing stroke recovery. By addressing the underlying vascular issues, these surgical interventions play a vital role in minimizing the damage caused by stroke and optimizing patient outcomes.
However, it is important to emphasize that the decision to undergo vascular surgery should be made in consultation with a multidisciplinary medical team. This team, consisting of neurologists, vascular surgeons, and interventional radiologists, evaluates various factors such as the type of stroke, location of the blockage, time since the stroke occurred, and the patient’s overall health. Their expertise and comprehensive assessment help determine the appropriateness of vascular surgery for each individual case.
As research and advancements in the field of vascular surgery continue, we can expect further refinements and innovative techniques to improve stroke treatment outcomes. Ongoing studies and technological advancements aim to enhance the efficacy and safety of vascular surgical interventions, providing even better results for stroke patients.
Ultimately, vascular surgery holds significant promise in the management of stroke, offering hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected by thy symptoms of stroke. By restoring blood flow, reducing the risk of recurrent strokes, and promoting efficient stroke recovery, vascular surgery plays a crucial role in minimizing the impact of stroke and helping patients regain their independence and overall well-being. As medical knowledge and techniques evolve, vascular surgery will continue to play an increasingly important role in the comprehensive treatment approach for stroke, contributing to improved outcomes and a brighter future for stroke patients worldwide.
