Peripheral Arterial Disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
May 29, 2023What is Peripheral Arterial Disease?
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD), is a common circulatory problem in which the arteries that carry blood to the legs and feet become narrow or blocked. This can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, cramping, and weakness in the legs, as well as slow healing of wounds and sores on the feet and legs. This condition occurs when there is a blockage or narrowing of the arteries in the legs, reducing the blood flow to the muscles and other tissues. PAD is a common circulatory problem that affects millions of people worldwide, especially elderly generations.
Peripheral Arterial Disease can be caused by a variety of factors, such as smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a family history of heart disease. Individuals who are obese or have a sedentary lifestyle are also at risk of developing PAD. It is essential to be aware of the symptoms of PAD to receive timely treatment and prevent serious complications.
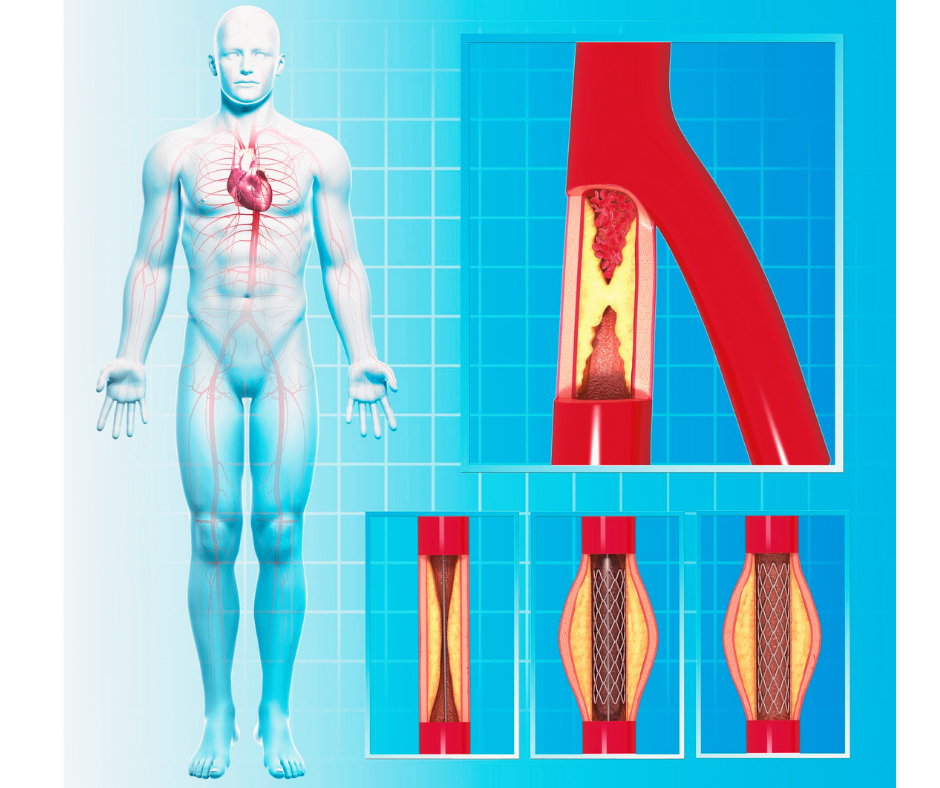
In this article, we will discuss the following topics:
Recognizing the Symptoms of PAD:
Explore the telltale signs of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and understand how it manifests in the legs and feet. Learn about the pain, cramping, weakness, and other symptoms that may indicate the presence of PAD. Early recognition is crucial for prompt medical intervention.
Diagnosis: Unraveling the Mystery of PAD:
Discover the diagnostic procedures employed by healthcare professionals to confirm the presence of PAD. From physical examinations and ankle-brachial index (ABI) test to advanced imaging techniques, explore the methods used to accurately diagnose this circulatory condition.
Unraveling the Causes and Risk Factors:
Delve into the underlying causes of PAD and understand the risk factors associated with its development. From smoking and diabetes to high blood pressure and high cholesterol, explore how these factors contribute to the narrowing or blockage of arteries in the legs.
Treatment Options for PAD:
Learn about the array of treatment options available for managing and alleviating symptoms of Peripheral Arterial Disease. From lifestyle modifications and medications to minimally invasive procedures and surgical interventions, discover the comprehensive approaches that healthcare professionals employ to address PAD effectively.
Preventing PAD and Promoting Leg Health:
Explore practical strategies and lifestyle changes that can help prevent the onset or progression of PAD. Discover the importance of maintaining a healthy weight, adopting an exercise routine, managing chronic conditions, and making informed choices to optimize vascular health.
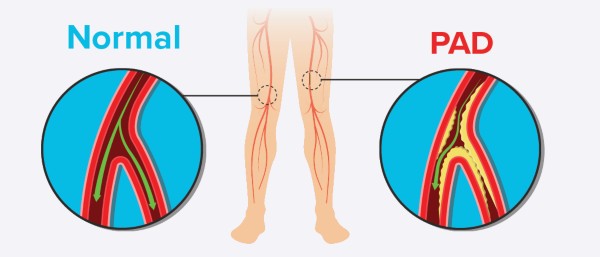
Symptoms of Peripheral Arterial Disease
The symptoms of PAD may vary depending on the severity of the condition: some people with PAD may have no symptoms at all, while others may experience one or more from the following symptoms:
Numbness or Weakness: Listen to Your Legs
Examine the sensation in your legs and be attentive to any feelings of numbness or weakness. These subtle signs can be early indicators of compromised blood flow due to PAD.
Coldness: When Feet and Legs Feel Chilled
Pay attention to temperature differences in your body. If you consistently experience coldness in your legs or feet, even when compared to other parts of your body, it could be a sign of impaired blood circulation associated with PAD.
Wounds that Refuse to Heal: A Cause for Concern
Slow healing of wounds or sores on the feet and legs should not be ignored. If you notice that injuries take an unusually long time to heal or don’t heal at all, it may be an indication of restricted blood flow caused by PAD.
Unveiling a Potential Link: PAD and Erectile Dysfunction
Discover a lesser-known connection between PAD and erectile dysfunction in men. Learn how impaired blood flow to the lower extremities can also affect blood flow to the male reproductive organs, highlighting the importance of considering PAD as a potential cause.
Hair Loss and Shiny Skin: Clues on Your Feet
Notice any changes in hair growth on your feet and legs. Reduced hair growth or even hair loss, along with shiny skin, can be indicative of compromised blood flow associated with PAD.
Pulse Check: Weak or Absent Pulses
Conduct a pulse check in your legs and feet. If you notice weak or absent pulses in these areas, it may suggest restricted blood flow due to PAD.
The Painful Reality: Activity-Induced Leg Pain
Explore the discomfort experienced during physical activities like walking or climbing stairs. If you notice pain and cramping in your legs that subsides after a few minutes of rest, it could be an indication of PAD.
Stubborn Sores: Watch Out for Non-Healing Wounds
Be vigilant about any non-healing sores or wounds on your toes, feet, or legs. These persistent ulcers can be a red flag for PAD and require medical attention.
If left untreated, PAD can cause serious complications, including tissue death, infections, and gangrene. In more severe cases, PAD can lead to amputation of the affected limb. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above.
Diagnosing Peripheral Arterial Disease
If you are experiencing symptoms of PAD, your doctor may perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history. They may also recommend one or more of the following tests:
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI): This test compares the blood pressure in your ankle to the blood pressure in your arm. A lower ratio may indicate PAD.
- Doppler ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the blood vessels in your legs and feet. It can help identify blockages and narrowings.
- Angiography: This test uses contrast dye and X-rays to create detailed images of the blood vessels in your legs and feet. It can help identify blockages and narrowings.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the blood vessels in your legs and feet. It can help identify blockages and narrowings.
Once a diagnosis of PAD is made, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan.
Treating Peripheral Arterial Disease
The goal of treatment for PAD is to improve blood flow to the legs and feet, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. Depending on the severity of your condition, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes to your diet, exercise routine, and smoking habits can help improve blood flow and reduce symptoms of PAD. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, as well as engaging in regular physical activity and quitting smoking, can all help improve your overall health and reduce your risk of complications.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications to help improve blood flow, reduce blood pressure, or lower cholesterol levels. Some medications may also help reduce pain and other symptoms of PAD.
- Angioplasty and stenting: This procedure involves inserting a small balloon into the blocked artery and inflating it to widen the artery and improve blood flow. A stent may also be inserted to help keep the artery open.
- Bypass surgery: In some cases, a bypass graft may be used to reroute blood around a blocked artery. This procedure involves using a vein from another part of your body or a synthetic tube to create a new pathway for blood flow.
- Endarterectomy: This procedure is used to remove the buildup of plaque or fatty deposits from the lining of an artery. The procedure is typically performed on patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) in the legs to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of complications. During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the affected artery and removes the plaque, restoring the normal diameter of the vessel and improving blood flow. Endarterectomy is a highly effective treatment option for patients with PAD, but it is typically reserved for those with severe blockages or those who have not responded well to other treatments.
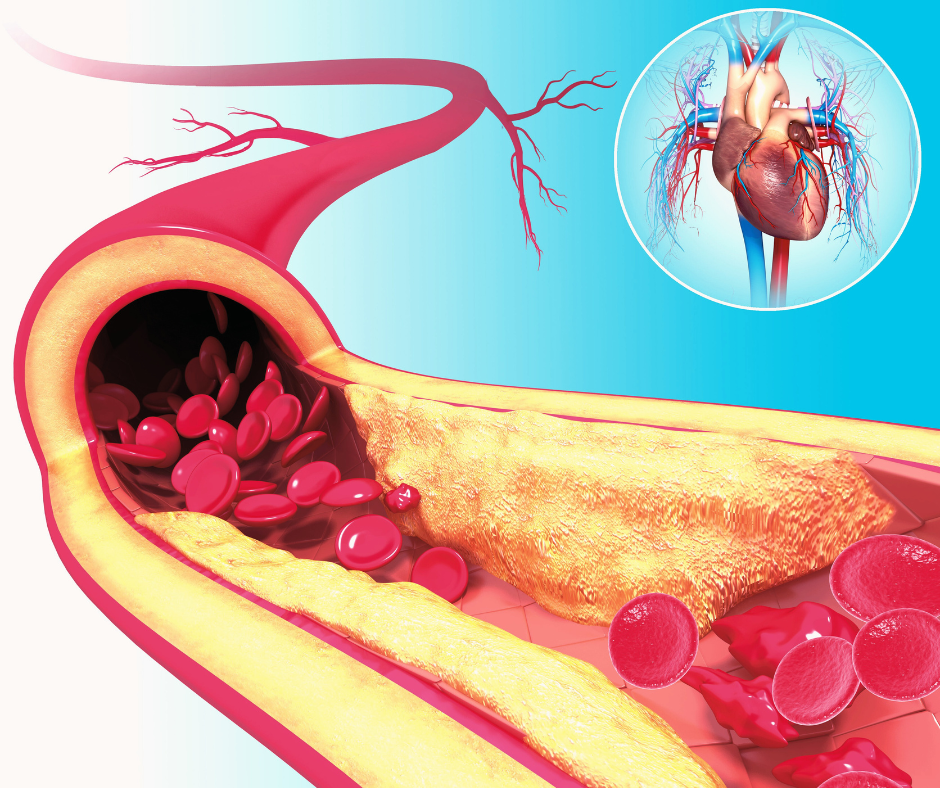
Preventing Peripheral Arterial Disease
Preventing PAD involves making lifestyle changes that reduce the risk factors associated with the condition. Here are some of the steps you can take to prevent PAD:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for PAD, and quitting smoking is the most crucial step in preventing the disease.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing PAD, so maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential.
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol: High blood pressure and high cholesterol can damage the arteries and increase the risk of PAD. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels regularly and take medications as prescribed.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can improve blood flow and reduce the risk of developing PAD.
- Manage diabetes: If you have diabetes, it is crucial to manage your blood sugar levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication.
In conclusion, Peripheral Arterial Disease is a common condition that affects the arteries in the legs, reducing blood flow.
